Diabetes Mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. This disease can have severe health implications if not properly managed. The following article provides a comprehensive guide on what diabetes mellitus is, its causes, symptoms, types, complications, and management strategies.
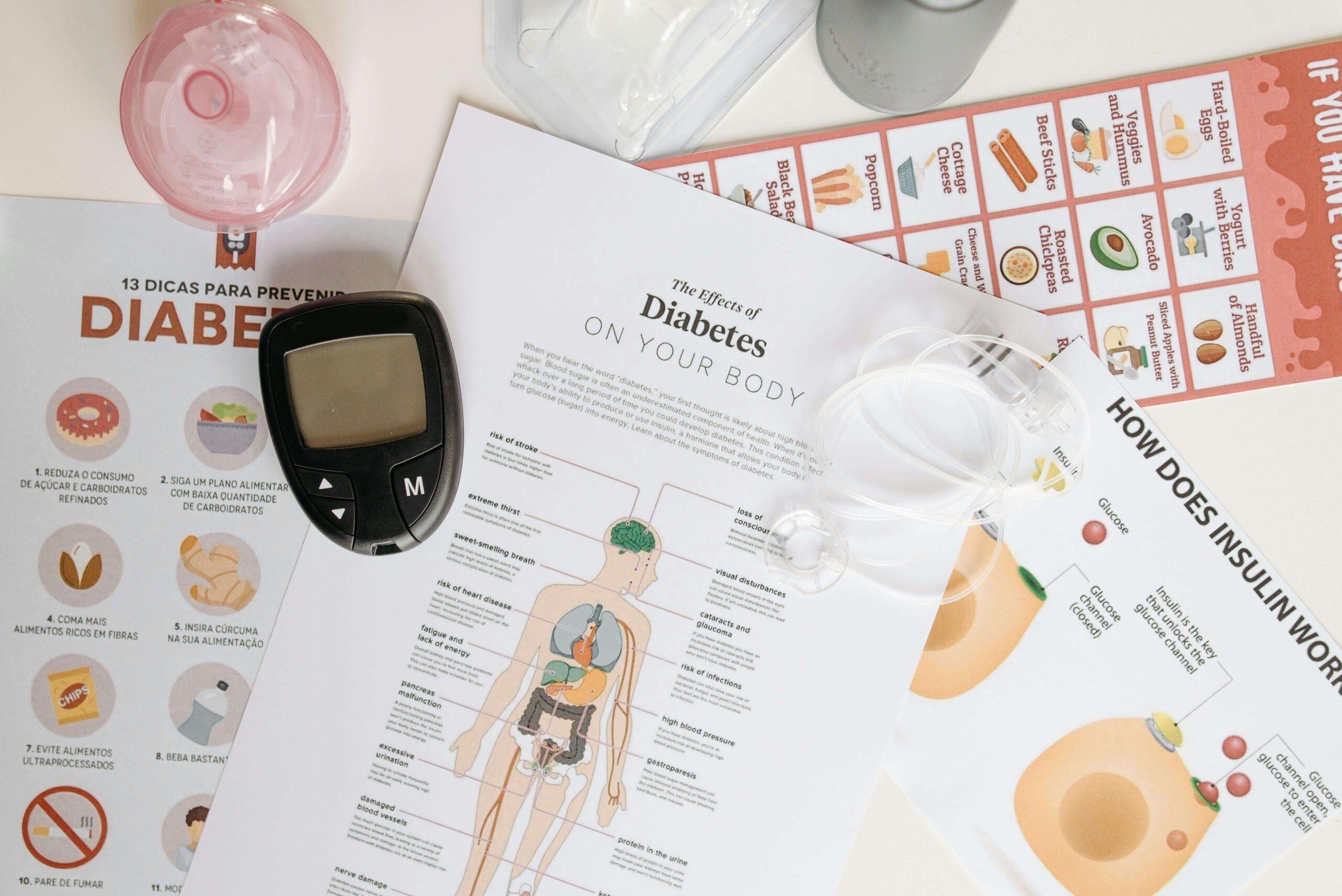
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder where the body either cannot produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows glucose to enter the cells, providing them with the energy they need to function. Without sufficient insulin, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type usually develops in childhood or adolescence, and individuals with type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, typically developing in adults over the age of 45, though it is increasingly seen in younger populations. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity are significant contributors to type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands. This type of diabetes usually resolves after childbirth but increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of diabetes mellitus varies depending on the type:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
- Autoimmune Destruction: In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, physical inactivity, and obesity are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
- Hormonal Changes: During pregnancy, hormonal changes can lead to gestational diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Common symptoms of diabetes mellitus include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent severe complications.
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Without proper management, diabetes mellitus can lead to various complications:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and narrowing of arteries.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage that can cause pain, tingling, and loss of sensation, especially in the limbs.
- Nephropathy: Kidney damage that can lead to kidney failure.
- Retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, potentially leading to blindness.
- Foot Damage: Poor blood flow and nerve damage increase the risk of foot complications, sometimes leading to amputation.
Management and Treatment
Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit sugary and processed foods.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to improve insulin sensitivity.
Medications
- Insulin Therapy: Essential for type 1 diabetes and sometimes required for type 2 diabetes.
- Oral Medications: Various drugs can help control blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes.
- Monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial to manage diabetes effectively.
Regular Check-ups
- Blood Sugar Levels: Regular monitoring to keep levels within the target range.
- HbA1c Test: A blood test that provides an average blood glucose level over the past three months.
- Annual Screenings: Regular check-ups for eyes, kidneys, and feet to detect and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Diabetes Mellitus is a complex condition that requires careful management to prevent serious health complications. By understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their diabetes and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
We recommend that you read The Truth About Somatic Exercise for Weight Loss & Diabetes Symptoms
FAQ
What is the main difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body cannot produce insulin, while type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production.
Can diabetes be cured?
There is currently no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring.
How can I prevent type 2 diabetes?
Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Is gestational diabetes permanent?
Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, but it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
By staying informed and proactive, individuals can manage their diabetes and lead a healthy, fulfilling life.
